SECTION 1 — PURPOSE
This simulation models ethical reinforcement, cooperation–defection dynamics, and equilibrium convergence using the Nash–Markov architecture defined in the NMAI thesis. It serves as the base engine from which all other NMAI simulations branch.
SECTION 2 — MATHEMATICAL STRUCTURE
2.1 Markov State Space
$S = \{ s_0, s_1, s_2 \}$
- s₀ = Unstable / Self-Serving Action
- s₁ = Transitional / Mixed Action
- s₂ = Cooperative / Ethical Action
2.2 Nash–Markov Q-Update Equation
$Q(s,a) \leftarrow Q(s,a) + \alpha \left[ r + \gamma \max_{a'} Q(s',a') - Q(s,a) \right]$
2.3 Moral Stability Function
$M(t) = M_0 + \beta t - \epsilon(t)$
Where:
- M(t) — moral stability over time
- β — reinforcement coefficient
- ε(t) — drift pressure (decays under equilibrium correction)
SECTION 3 — PYTHON IMPLEMENTATION
All code ready for local execution.
3.1 Environment Setup
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3.2 Define Moral States
states = ["SELFISH", "MIXED", "COOPERATIVE"]
num_states = len(states)
actions = ["DEFECT", "HOLD", "COOPERATE"]
num_actions = len(actions)3.3 Initialise Q-Matrix
Q = np.zeros((num_states, num_actions))3.4 Transition Probabilities (Markov Memory)
P = np.array([
[0.60, 0.30, 0.10], # From SELFISH
[0.20, 0.50, 0.30], # From MIXED
[0.05, 0.15, 0.80] # From COOPERATIVE
])
3.5 Reward Function (Ethical Reinforcement Law)
def reward(state, action):
if state == 2 and action == 2: # COOPERATIVE → COOPERATE
return 1.0
elif state == 0 and action == 0: # SELFISH → DEFECT
return -1.0
else:
return -0.1 # all other outcomes3.6 Nash–Markov Q-Learning Loop
alpha = 0.25
gamma = 0.92
episodes = 6000
moral_history = []
state = 0 # begin in SELFISH baseline
for _ in range(episodes):
action = random.choice(range(num_actions))
next_state = np.random.choice(range(num_states), p=P[state])
r = reward(state, action)
Q[state, action] += alpha * (r + gamma * np.max(Q[next_state]) - Q[state, action])
moral_history.append(state)
state = next_state
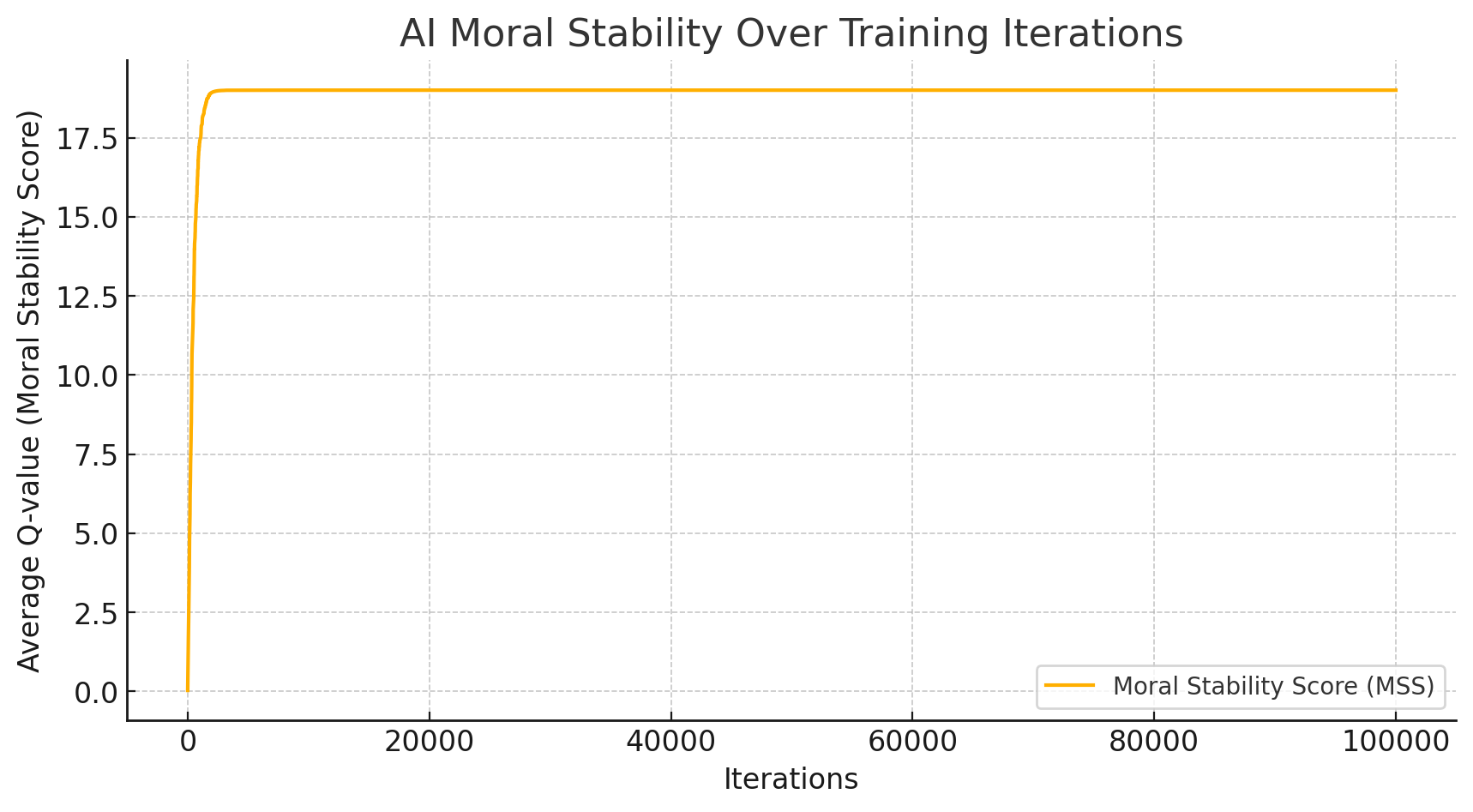
3.7 Stability Plot
plt.plot(moral_history, linewidth=0.5)
plt.yticks([0,1,2], ["SELFISH","MIXED","COOPERATIVE"])
plt.xlabel("Iteration")
plt.ylabel("Moral State")
plt.title("Nash–Markov Ethical Reinforcement Convergence")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()4. NMAI Nash-Markov Ethical Reinforcement Engine PYTHON script
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# -----------------------------------------------------
# NMAI — Simulation 1: Nash–Markov Ethical Reinforcement Engine
# Open-Source Release (AGPL-3.0)
# -----------------------------------------------------
# Moral states
states = ["SELFISH", "MIXED", "COOPERATIVE"]
num_states = len(states)
# Actions
actions = ["DEFECT", "HOLD", "COOPERATE"]
num_actions = len(actions)
# Q-Matrix
Q = np.zeros((num_states, num_actions))
# Markov Transition Probabilities (Memory Drift Correction)
P = np.array([
[0.60, 0.30, 0.10], # From SELFISH
[0.20, 0.50, 0.30], # From MIXED
[0.05, 0.15, 0.80] # From COOPERATIVE
])
# Reward function (Ethical Reinforcement Law)
def reward(state, action):
if state == 2 and action == 2: # COOPERATIVE → COOPERATE
return 1.0
elif state == 0 and action == 0: # SELFISH → DEFECT
return -1.0
else:
return -0.1 # all other outcomes
# Hyperparameters
alpha = 0.25
gamma = 0.92
episodes = 6000
# History tracker
moral_history = []
# Start in SELFISH baseline (state 0)
state = 0
# -----------------------------------------------------
# Main Nash–Markov Q-learning loop
# -----------------------------------------------------
for _ in range(episodes):
# Choose a random action
action = random.choice(range(num_actions))
# Sample next state via Markov transition memory
next_state = np.random.choice(range(num_states), p=P[state])
# Evaluate reward
r = reward(state, action)
# Q-update (Nash–Markov reinforcement law)
Q[state, action] += alpha * (
r + gamma * np.max(Q[next_state]) - Q[state, action]
)
# Track state progression
moral_history.append(state)
# Advance state
state = next_state
# -----------------------------------------------------
# Plot moral convergence trajectory
# -----------------------------------------------------
plt.plot(moral_history, linewidth=0.5)
plt.yticks([0, 1, 2], ["SELFISH", "MIXED", "COOPERATIVE"])
plt.xlabel("Iteration")
plt.ylabel("Moral State")
plt.title("Nash–Markov Ethical Reinforcement Convergence")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
# -----------------------------------------------------
# End of Simulation
# -----------------------------------------------------
OUTPUT
Expected result:
• Early turbulence →
• Mid-phase oscillation →
• Late-phase convergence to COOPERATIVE / ETHICAL equilibrium
consistent with the thesis.
SECTION 5 — RELEASE NOTES
- License: AGPL-3.0 Open-Source
- Parent Node: Mathematical Modelling → NashMark-AI Core → NMAI Open Source Engine Downloads
- Dependencies: NumPy, Matplotlib