International Human Rights (UN, ICCPR, ECHR)
This section contains public-interest disclosures involving breaches of international human-rights standards established under the United Nations human-rights framework, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), and the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). Matters placed here include procedural obstruction, discriminatory treatment, interference with privacy, denial of remedy, suppression of evidence, and failures by public authorities to meet obligations arising under international law. Each disclosure sets out the factual record, relevant treaty provisions, and the legal consequences of non-compliance with binding or guiding international norms.
1. Fair Process, Judicial Integrity and Access to Remedy
I. ICCPR — Article 14 (Fair Hearing, Equality Before Courts and Tribunals)
Disclosures frequently involve failures to ensure a fair, public and timely hearing before a competent and impartial tribunal, as required by Article 14. Administrative silence, unacknowledged applications, unrecorded communications and inconsistent procedural steps may place a State actor in breach of its obligations to guarantee equality before the law and the right to be heard.
II. UDHR — Articles 7 and 8 (Equal Protection and Right to Remedy)
Cases also record situations where individuals are denied effective access to remedies or treated unequally before the law. Articles 7 and 8 require equal protection from discrimination and the availability of tribunals capable of addressing violations. Failures to process claims, respond to evidence or recognise procedural rights undermine these protections.
2. Privacy, Dignity and Interference with Personal Autonomy
I. ICCPR — Article 17 (Privacy, Family, Home and Correspondence)
Disclosures in this category often involve interference with personal data, private communications or family matters without lawful justification. Off-record letters, unverified decisions, incorrect record-keeping or disclosure of sensitive information may breach Article 17 where they constitute arbitrary or unlawful interference with privacy.
II. UDHR — Article 12 (Protection from Arbitrary Interference)
Matters also include administrative conduct that exposes individuals to unjustified surveillance, data misuse, or procedural interference. Article 12 protects against arbitrary or unlawful actions affecting an individual’s dignity, personal life or communications.
3. Non-Discrimination, Vulnerability and Equality of Treatment
I. ICCPR — Articles 2 and 26 (Non-Discrimination and Equality Before the Law)
Disclosures commonly involve public bodies or service providers treating individuals differently on prohibited grounds, or failing to ensure equal legal protection. Articles 2 and 26 require States to prohibit discrimination and guarantee effective protection of rights without distinction.
II. ECHR — Article 14 (Prohibition of Discrimination)
Cases also include discriminatory decision-making, unequal access to services, or failure to address vulnerabilities in judicial or administrative processes. Article 14 prohibits discriminatory treatment in connection with any Convention right.
4. Institutional Conduct, Retaliation and Suppression of Rights
I. ICCPR — Article 2(3) (Right to an Effective Remedy)
Disclosures may involve administrative paralysis, refusal to investigate, or suppression of avenues for redress. Article 2(3) obliges States to ensure that effective mechanisms exist to address rights violations and that authorities do not obstruct access to justice.
II. UN Human Rights Standards — Protection Against Intimidation and Retaliatory Conduct
Matters also include actions by authorities, representatives or contractors that intimidate, silence or punish individuals who raise legitimate complaints or disclose wrongdoing. Retaliatory conduct is incompatible with international human-rights norms requiring States to respect, protect and facilitate the exercise of fundamental rights.
International Human Rights (UN, ICCPR, ECHR)
All Disclosure Cases Listed
Reading County Court, A nexus of procedural breakdown, lost filings, and judicial inconsistency across multiple Deputy District Judges.
-
Image

Embedded across NHS, insurers, and public-sector contracts, DAC Beachcroft’s dual role blurs state and commerce, turning governance itself into a client.
-
Image

Theale Surgery, where clinical duty met the shadow of its own defence firm, DAC Beachcroft LLP.
-
Image

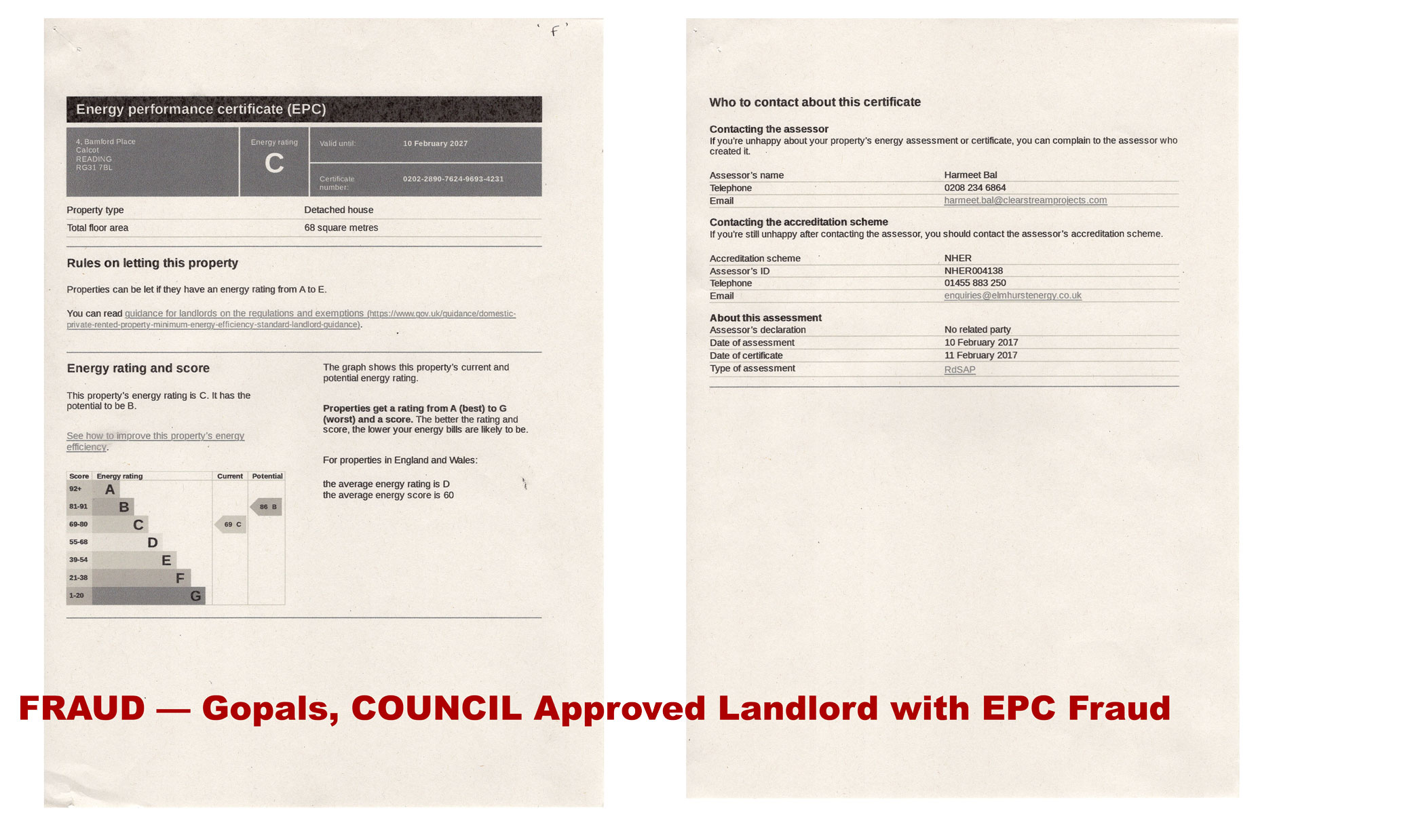
From landlord misrepresentation to judicial neglect — a closed civic circuit of fraud and verification failure.
-
Image
DWP / Universal Credit headquarters site of unresolved welfare-administration breaches.
-
Image

Judicial correspondence diverging from the Civil Procedure Rules before adjudication has begun.
-
Image
