Commercial / Corporate Law
This section contains public-interest disclosures arising from the conduct of companies, corporate officers, insurers, lenders, agents, and commercial entities whose actions have breached statutory duties, contractual obligations, regulatory requirements, or industry standards. Matters placed here include failures of corporate governance, unfair commercial practices, unlawful trading activity, financial irregularities, and the misuse of corporate authority in dealings with consumers, clients, and counterparties. Each disclosure provides the documentary record, communications, statutory framework and breach analysis required to identify the commercial or corporate law issues engaged.
1. Corporate Misconduct and Governance Failures
I. Companies Act 2006 — Directors’ Duties (Sections 171–177)
Disclosures in this category commonly relate to failures of directors or corporate officers to act within their powers, exercise reasonable care and skill, avoid conflicts of interest, or comply with duties of good faith and proper purpose. Conduct that places personal or organisational advantage above statutory duties is recorded here, together with the evidence demonstrating breach.
II. Fraud Act 2006 — False Representation and Abuse of Position
Cases also include actions where commercial entities have made false statements, concealed key information, or used their corporate position to cause loss, gain advantage, or manipulate contractual outcomes. These behaviours fall under Sections 2 and 4 of the Fraud Act and carry both civil and criminal liability.
2. Commercial Dealings and Trading Standards
I. Business-to-Business Contractual Breach
Disclosures include failures to deliver contractual services, deliberate obstruction of agreed terms, unnotified variation of commercial obligations, and conduct calculated to frustrate or prevent performance. These cases are grounded in the principles of English commercial contract law requiring adherence to expressed and implied terms.
II. Competition Act 1998 — Abuse of Dominance and Anti-Competitive Conduct
Some matters engage Section 18 prohibitions on conduct that distorts competition, exploits market position, or restricts fair dealing. Evidence may include exclusionary tactics, refusal to supply, or discriminatory commercial practices.
3. Financial Irregularities and Regulatory Non-Compliance
I. Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (FSMA) — Regulated Activity and Disclosure Duties
Disclosures within this category include failures by firms carrying out regulated activities to meet obligations relating to transparency, disclosure, accuracy of information, and lawful conduct. Breaches of FSMA can invalidate transactions and attract regulatory sanction.
II. FCA Handbook — Principles for Businesses (PRIN)
Cases also arise where commercial entities have failed to act with integrity, failed to treat customers fairly, or failed to exercise due skill, care and diligence. These failings breach PRIN 1–6 and reflect systemic governance deficiencies within the firm.
4. Corporate Communication, Notice Obligations and Document Handling
I. Companies Act 2006 — Statutory Record-Keeping and Notice Requirements
Disclosures include failures to maintain accurate statutory registers, failure to issue required notices, defective documentation, unserved communications, or records inconsistent with legal requirements. Such omissions undermine transparency and breach obligations imposed on companies regarding their administrative conduct.
All Disclosure Cases Listed
Embedded across NHS, insurers, and public-sector contracts, DAC Beachcroft’s dual role blurs state and commerce, turning governance itself into a client.
-
Image

Service by unapproved channel during active proceedings a departure from rule-based process.
-
Image
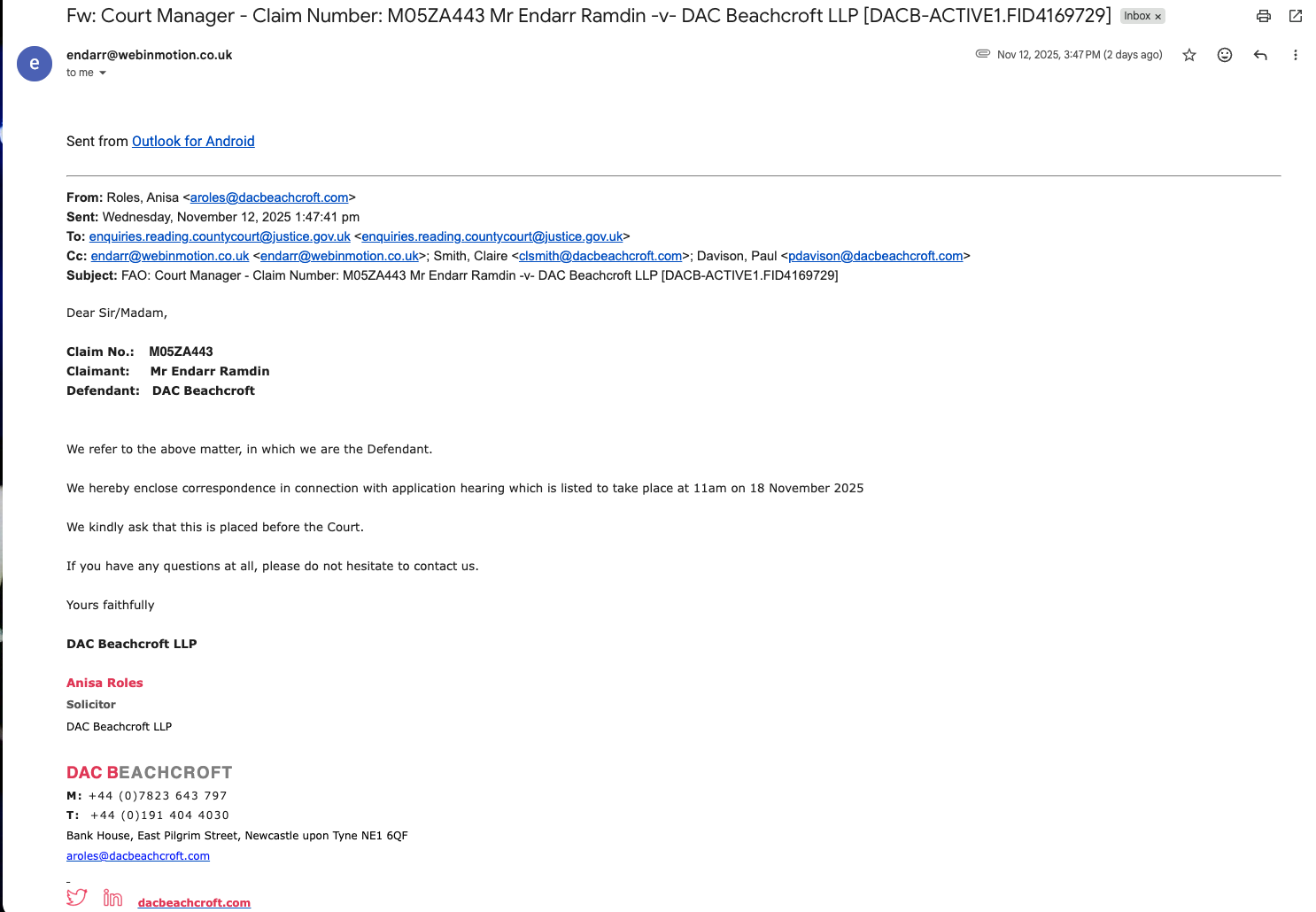
A skeleton argument served into a silent court — evidence of procedural interference layered on top of judicial freeze.
-
Image
